Introduction
Note: This activity assumes that you have a working knowledge of Scratch and how it is laid out. If not, you should first go through our “Introduction To Animation And Movement In Scratch” module to learn Scratch-specific vocabulary and about Scratch’s block-based coding system.
The purpose of this tutorial is to build upon some of the movement techniques introduced in the “Basic Movement Techniques” tutorial by integrating some elements of physics to make the controls feel more realistic. In the “Basic Movement Techniques” tutorial, we looked at three ways to control a player sprite that all moved the sprite directly and by a fixed amount, either by changing the sprite’s x and y coordinates or by using the “Move steps” block. In this tutorial, you will be learning about movement controls that move a sprite with acceleration, speed, and friction, instead of a fixed movement distance. Many games incorporate some elements of physics in their control and gameplay. In Nintendo’s Super Mario World, for example, Mario can run faster or slower depending on the player pressing a “Run” button, and he takes time to reach his top speed as well as to come to a complete stop.
Games can use more complex controls to create a wider variety of gameplay experiences with the end result hopefully being more fun and interesting for players. Finding the right combination of numbers for acceleration, top speed, and friction that feel “good” for a player to control requires some experimentation. In this activity, you will also learn to use variables to set up your game environment which will allow you to quickly make changes to what you will set for your acceleration, top speed, and friction.
This activity has three main parts and will cover:
- Using a variable to keep track of speed
- Adding a variable for acceleration
- Slowing down a sprite with friction
Learning Goals
- Understand how acceleration, speed, and physics can be used to control sprite movement in Scratch.
- Learn to use variables to define and tune a game environment in Scratch.
Vocabulary
Acceleration - Acceleration is the rate of change of speed. A positive acceleration is speeding up/getting faster and a negative acceleration is slowing down/getting slower. A negative acceleration is also called deceleration.
Friction - Friction is resistance to movement that happens when things rub against each other. Friction reduces speed.
Speed - Speed is how fast something is moving. Speed can be increased by positive acceleration or decreased by negative acceleration.
Variable (programming) - A variable is a way to refer to and store data, such as numbers or text.
Guiding Questions
- How do acceleration and friction affect speed?
- Potential answer(s): acceleration increases speed; friction decreases speed; friction can limit the top/maximum speed achievable, depending on acceleration; friction makes things eventually stop moving if no new acceleration is added.
- How is controlling a sprite with acceleration, friction, and speed different than controlling the position of a sprite directly?
- Possible answer(s): when you’re controlling a sprite directly, they stop moving the instant that you let go of the keys that you’re pressing; when you’re using a simulated physics model, you have to think about how increasing and decreasing speeds gradually might affect your control.
Curriculum Links
- Computer Science
- Math (percentage/proportion)
- Physics (acceleration, speed, friction)
Materials
Scratch (online or desktop)
Computer Activity
The example that we will be building is based on the “tank controls” scheme discussed in the “Basic Movement Techniques” activity. It’s a good control scheme to start with since you’ll only have to deal with forward and backward movement, while you can still handle rotation by directly changing the direction of the player sprite. First, though, we’ll go over the relationship between acceleration, speed, and friction in concept before you make them in Scratch.
Acceleration, speed, and friction
Acceleration, speed, and friction are all related to moving things:
- Acceleration is about getting things moving. In a car, this is what pressing the gas pedal does. In our example, it will be used to increase speed, meaning it will control how fast the sprite gets faster.
- Speed is about how fast you move. In a car, this is how fast the car is going. In our example, it will be the distance that the sprite moves when the “Move steps” block is used.
- Friction is about stopping movement. In a car, this is what pressing the brake pedal does. In our example, it will be used to decrease the sprites speed, that is, to lower the number of steps moved when the “Move steps” block is used.
Take a look at the tank controls example below, taken from the “Basic Movement Techniques” tutorial: what do you think the acceleration, speed, and friction values are? For this, only consider the “Move steps” blocks.
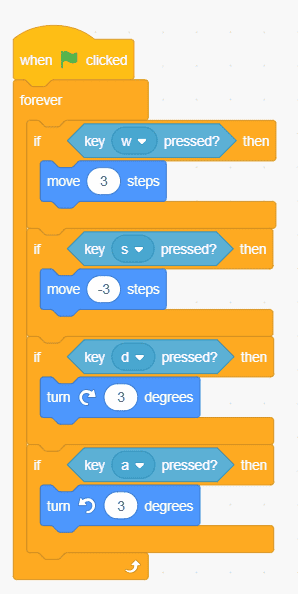
Speed is probably the most obvious one and you can find it by looking at the “Move steps” blocks. In this case, the sprite moves forward at a speed of 3 units when the W key is pressed or backward at a speed of 3 units when the S key is pressed. Acceleration and friction are a bit trickier, because they aren’t apparent in the way that this control scheme has been set up, so we’ll describe how they impact the movement of the sprite instead: the sprite starts moving the instant you press a key, but only ever goes as fast as 3 units, and the sprite stops moving the instant you stop pressing either the forward or backward movement keys.
Side bar: Units of measure
If you think about speed limits for cars, though, you’d notice that there’s something missing: car speed is reported in kilometers per hour, so from that, you can see that speed is a measure of the amount of distance covered in a certain amount of time. You can see that the distance would be 3 units, but what is the unit of time for this in Scratch? How often does your sprite move 3 units? The answer is that it updates once per “frame”, which is usually around 1/30th of a second. This is because Scratch tries to run at a fixed frame rate of 30 frames per second, that is, redrawing the stage 30 times per second to update costumes or the positions of sprites.
Using a variable to keep track of speed
You might be wondering how you can get the speed of a sprite when Scratch only tracks position and direction. Because Scratch doesn’t have physics simulation built-in, you’ll need to create a variable to track it. What you’re trying to do is replace the fixed speed in the code above with a new variable called speed. Only worry about forward speed for now. Before looking at the code below, try doing it yourself. Remember, to create a variable, go to the Variable category in Scratch near the bottom of the categories and click on “Make a variable”.
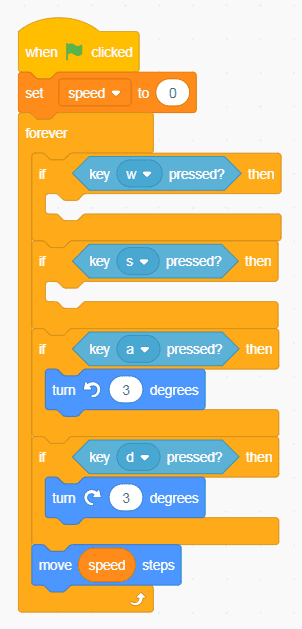
You can try testing it out, but it definitely won’t make your sprite move. A few things to notice in the code above:
- If you look at the If block that checks if W is pressed, you’ll see that there’s no action in there yet.
- I’ve created a new variable and named it “speed”. It went where the 3 was in the “Move steps” block.
- My “speed” variable gets set to 0 every time the green flag is clicked. I don’t want my sprite to already be moving when everything starts.
- The “Move steps” block is now at the bottom, after all the key detection. As I mentioned earlier, you won’t be directly changing the position of the player sprite any more.
What action do you think would make the sprite move forward if the “W” key were pressed? As it’s currently set up, you would need some way to increase the “speed” variable. Is there a block for that already? Try to find the block that would change the value of a variable by an amount before looking at the code below.
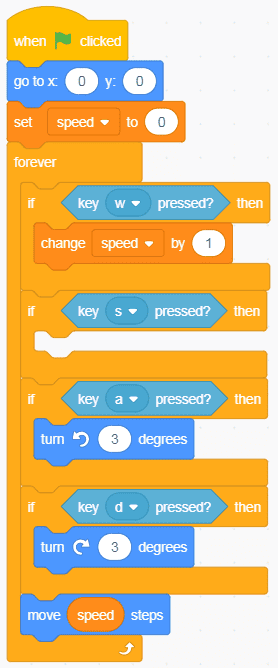
You can use Scratch’s “Change variable by” block to increase the speed variable by 1 as long as the “W” key is pressed. I also added a “Go to x and y” block to reset the position of the sprite to the centre of the stage each time, but this isn’t absolutely necessary. As an exercise, try using different values with the “Change variable by” block. What happens with larger numbers?
In the code below, I’ve gone ahead and added a “Change variable by” for an action when the “S” key is pressed. Since I want this to go in the opposite direction of the “W” key, I will use -1. Try doing this yourself before checking the code below.
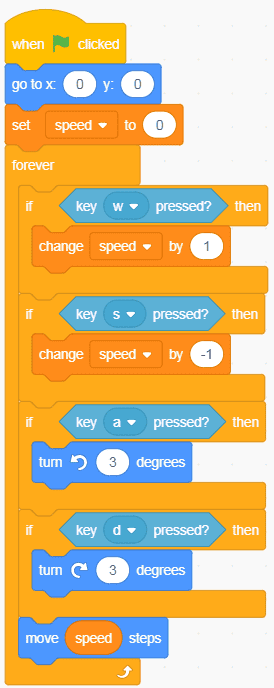
Adding a variable for acceleration
Just like I replaced the fixed value of the “Move steps” block, I want to also use a variable for acceleration. This is for a different reason than the speed, since we will be keeping this number constant: looking at the code above, where might be use a variable for acceleration? Remember that acceleration is the rate at which speed changes. Try creating a variable for acceleration and putting it in where you think it should go, before looking at the code below.
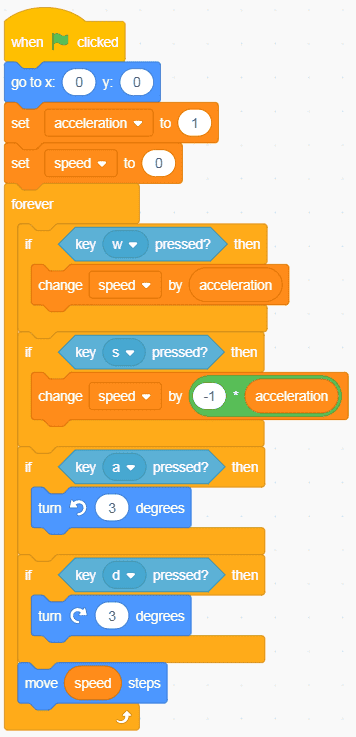
I’ve added four blocks to that code:
- I’ve added a “Set variable to” block for acceleration, and I’ve set it to 1.
- I’ve replaced the amount that we’re changing the speed variable when pressing “W”/forward with the acceleration variable.
- I’ve replaced the amount that we’re changing the speed variable when pressing “S”/backward with the acceleration variable and a multiplication operator block.
- In the multiplication operator, I’m multiplying by -1 because I want the same acceleration rate going backward as going forward.
Now, if you want to change the acceleration value, you only need to change it in one place, the “Set variable to” block, instead of in two. This has the added benefit of allowing you to use a slider to adjust the value and to try different values. To do this:
- Right-click on the “acceleration” variable display that should have been made when you created the acceleration variable.
- Click on “slider” to be able to have a slider to adjust the value of the acceleration variable.

If you clicked on slider, your acceleration variable display should look as below:
Slowing down a sprite with friction
As of right now, unless you use “W” and “S” to get your sprite’s speed back to 0, your sprite will continue on indefinitely. I will be creating and using a variable called “friction” to slowly decrease the speed of a sprite. Think of this like a car rolling to a stop. The way that you will be using friction in this activity is as a percent decrease of speed. So, for example, if I have a friction value of 5, the sprite’s speed decreases by 5%.
This does get a bit more complex than acceleration and speed, so I want you to start by creating a “friction” variable and turning on its slider. The slider will be crucial later to be able to tune the amount of friction on the fly. Once you’ve done that, you can try setting up the blocks that you think you’ll need, keeping in mind that what you’re trying to do is to reduce speed by a certain percentage. Check the code below to see how I approached it.
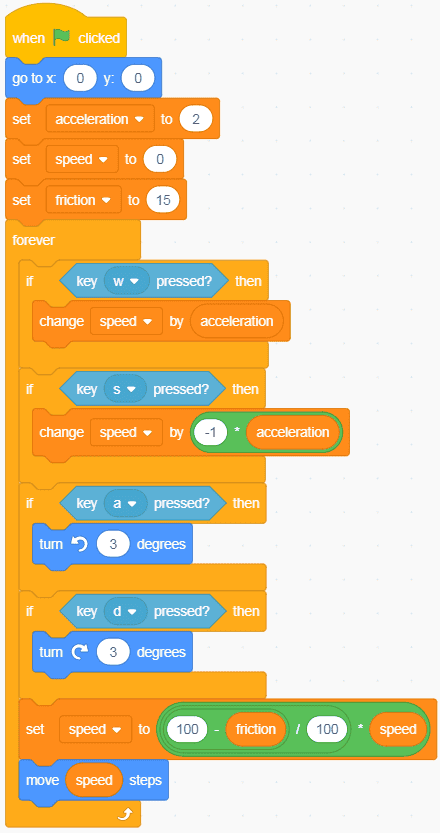
Comparing this code to the last version, I want to point out a few things:
- I’ve used a “Set variable to” block at the beginning to set my friction variable to 15. A lower number here means less friction and so less slowing. A higher number here means more friction and so greater slowing.
- I’ve used the “Set variable to” block to adjust the speed variable by a percentage. The percentage amount is set by what the friction variable is set to.
- Pay attention to how the math operator blocks are nested:
- 100 minus the friction variable (e.g. 100 – 15 = 85)
- The above number is divided by 100 (e.g. 85 / 100 = 0.85)
- The calculated number is multiplied with the speed variable
There are a couple ways to think about that math for the friction speed reduction, but an easy way to check if it’s working is to test it out with a few easy numbers, for example:
- If friction is zero (0), that math becomes 1 times the speed variable, which means speed doesn’t change.
- If friction is 100, that math becomes 0 times the speed variable, which means that speed is always zero.
- If friction is 50, that math becomes 0.5 times the speed variable, which means that speed is reduced by half each time the sprite moves.
After that, experiment with both the friction and acceleration sliders to find what you think would be a “good” amount of acceleration and friction.
Conclusion
The concepts of acceleration and friction presented above are simplified versions of more complex physical systems. Acceleration isn’t necessarily a fixed number: it might be easier to accelerate at lower speeds, for example, or harder to accelerate at higher speeds. Friction likewise isn’t necessarily a constant percentage: it might depend on the weight of the moving object, for example, or the roughness of the surfaces that are rubbing. On the other hand, more complex systems aren’t necessarily better than simple systems. It all depends on what you’re trying to achieve. In some games, such as Mobius Digital’s Outer Wilds, accurate or realistic physics models are a big part of their gameplay. Other games, like Matt Makes Games’ Celeste, don’t try to use realistic physics, instead tuning the controls so that they offer more control for their gameplay. In the end, sometimes a simplified physics model is what you’re looking for, for the right balance between fun and complexity.
Additional Resources
- Learning space: Introduction To Animation And Movement In Scratch
- Learning space: Player control in Scratch: Basic Movement Techniques (http://rootandstem.ca/learn/pinnguaq-at-home-april-20th-25th/player-control-in-scratch-movement-techniques-1)
- The Scratch Wiki, an invaluable resource and starting point for addressing questions about specific Scratch blocks. (https://en.scratch-wiki.info/wiki/Scratch_Wiki_Home)
- Scratch (https://scratch.mit.edu/)
Social Media Resources
Official Scratch Twitter @scratch
